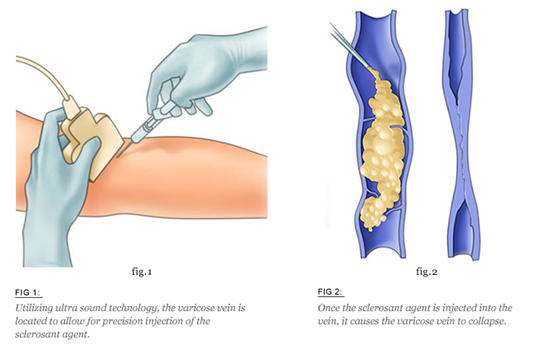
Ultrasound guided Foam Sclerotherapy (UGFS) is a new treatment also known as endovenous chemical ablation that involves injections of dilated veins, including major refluxing trunks (saphenous vein) or larger underlying abnormal veins which would not normally be treated with conventional sclerotherapy. This is performed under ultrasound control using foam chemical irritant in order to damage the internal lining of the vein and eventually collapse and seal shut the veins. A sterile solution called sclerosant (Polidocanol injectable foam or Varithena) is injected into the lumen of the target veins using a needle or a single cannula. The solution serves as an irritant to the vein lining causing it to undergo fibrosis and eventually disappear over time. More than one vein may be injected at each session. This procedure can be performed with or without local anesthesia, and there is minimal pain involved.
Foam sclerotherapy has been shown to be more effective than liquid. It is becoming an increasingly popular choice in the management of patients with recurrent varicose veins or adjuvant treatment to endovenous ablation of the reflux. Repeat treatment may be considered an integral part of UGFS in some of the treated patients. Procedure may be performed in outpatient setting and patients are able to walk immediately, resuming work the following day. Post-procedural graduated compression with elastic stocking is required for a short period of time.